Here you will find summarised information on some of the more common oral health conditions. Please note that not all of the dental and surgical conditions we treat are included at this point and that we are continually adding on to this list.
The information provided is meant purely for educational purposes and may not be used as a substitute for medical diagnosis or treatment. You should seek the advice of your dentist or a qualified oral healthcare provider before starting any treatment.
In cases where teeth are badly broken-down, restorations such as inlays, onlays and crowns may be necessary.
Inlays and onlays are indirect restorations (fillings) that are fitted to a cavity in a tooth and cemented into place. A crown is an indirect restoration which completely covers or encircles a tooth and is also cemented into place.
Crowns can be made from many materials such as gold, ceramic, or a combination of both materials. Crowns are often used to protect the remaining tooth structure and to improve the appearance of the teeth.
Paediatric Dentistry deals with all aspects of oral care in children. These include the prevention, diagnosis and management of common dental diseases like caries and gum disease, the interception and early correction of minor malocclusions and the detection and management of dental anomalies and injury to children's teeth.
The paediatric dentists specialise in training young children to accept dental treatment. Children who would especially benefit from the long term care of a paediatric dentist include those who are at high risk of developing dental disease and children with special needs.
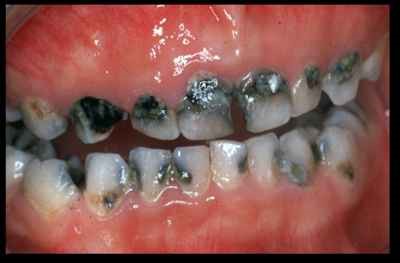 Early Childhood Caries
Early Childhood Caries
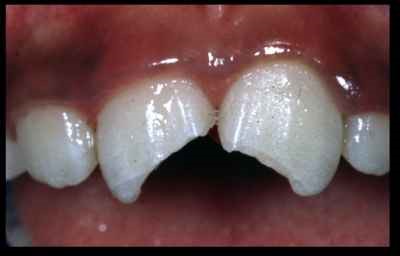 Fractured Upper Incisors
Fractured Upper Incisors
The paediatric dentists specialise in training young children to accept dental treatment. Children who would especially benefit from the long term care of a paediatric dentist include those who are at high risk of developing dental disease and children with special needs.
Crooked teeth may lead to psychosocial and oral hygiene difficulties, and can lead to improper bites which may limit one's bite efficiency and pronunciation.
Orthodontists are Dental Specialists who are trained in the guidance of jaw development and eruption of teeth. In addition, they are able to treat crooked teeth, improper bites and disproportionate jaw positions.
Advancements in the delivery of Orthodontic treatment have led to a variety of treatment options ranging from ceramic and metal self-ligating braces, lingual braces, clear aligner therapy and orthodontic micro-implants to accommodate the patient's lifestyle needs.
Veneers are thin custom-made shells made of tooth coloured materials such as ceramic or composite. They are placed over a damaged tooth surface to improve the aesthetics of the tooth and/or to protect the remaining tooth surface. Composite veneers may be built up directly in the mouth or indirectly fabricated in the dental laboratory.
Dental and maxillofacial implants (ear, nose and eye implant retained prosthesis, craniofacial implants) may be required.
Dentofacial deformities are conditions in which the upper or lower jaws are out of proportion to the rest of the face and head. These deformities also include cleft lip and palate deformities. These deformities not only present an aesthetic problem for patients, they can also result in chewing or biting problems as the upper and lower teeth do not meet properly.
Treating such deformities involves a multi-disciplinary team consisting of an oral and maxillofacial surgeon and an orthodontist.
To restore facial harmony, jaw (orthognathic) surgery may be performed by oral and maxillofacial surgeons to realign the jaws into a pleasing aesthetic appearance and to restore the proper bite.
Dental decay is an infectious process whereby bacteria damage the hard tooth structure.
The presentation of dental decay is highly variable. Initially, it can start out looking like a small chalky area but as the lesion progresses, it can turn brown and eventually present as a cavity. As the decay progresses towards the centre of the tooth, it can cause pain. The pain may worsen with exposure to heat, cold or sweet food. At times, the decay cannot be seen directly and radiographs are required to detect it.
Dental decay formation is caused by a combination of factors - teeth, bacteria, sugars and time. Bacteria produce acids when exposed to dietary sugars and this acid diffuses into the tooth, dissolving tooth material over time. Saliva helps to repair such damage by neutralising the acid if the acid attacks are infrequent. However, impaired salivary flow and the acidity of the saliva can increase the risk of dental decay.
Diagnosis involves the inspection of the teeth using a good light source. Large lesions can be detected with the naked eye but smaller lesions may be difficult to identify. Dental radiographs may also detect decay that cannot be visually seen, especially decay between the teeth.
For small early lesions, topical fluoride is sometimes used to encourage remineralisation of the tooth structure. For larger lesions, the progression of decay can be stopped by treatment. The decayed portions of the tooth are removed and a restorative material is placed to restore aesthetics and function. Restorative materials include amalgam, composite, porcelain and gold. In some cases, root canal/endodontic therapy may be required if the pulp in the tooth dies. If the tooth is too far destroyed for effective reconstruction, extraction may be recommended.
Good dental health can be achieved with proper daily brushing and flossing. The goal of brushing and flossing is to remove the bacteria containing plaque. Intake of dietary sugars should be monitored and regular examinations by dental professionals are recommended.
Dentofacial deformities are conditions in which the upper or lower jaws are out of proportion with the rest of the face and head. These deformities also include cleft lip and palate deformities.
These deformities not only present an aesthetic problem for patients, they can also result in chewing or biting problems as the upper and lower teeth do not meet properly. The treatment of such deformities involves a multi-disciplinary team comprising an oral and maxillofacial surgeon and an orthodontist.
To restore facial harmony, jaw (orthognathic) surgery may be performed by oral and maxillofacial surgeons to realign the jaws into a pleasing aesthetic appearance and to restore the proper bite.
Food, drinks, tobacco or tetracycline stains may be some of the causes for discoloured teeth. Patients who want to brighten their teeth can choose a teeth whitening treatment package suitable for them. Treatments range from a 1-hour in-office treatment to take-home kits.
Facial pain may have several causes and can be related to the hard and soft tissues in the face.
This pain can arise from the muscles (Myofascial Pain Dysfunction Syndrome), the jaw joint (Temporomandibular Joint Disorders) or even from the nerves of the face (Neuralgia).
These conditions can affect the eating habits and lifestyle of the patient. The treatment of such pain depends on the cause of the pain and the severity of the condition.
These conditions may be treated by different dental specialists. For example, pain from the muscles can be treated by a prosthodontist using conservative methods such as splint therapy, while severe pain from the jaw joints may require surgical intervention by an oral and maxillofacial surgeon.
Do your gums bleed when you brush? Or do you brush your teeth less than once a day? Are you concerned that your gums are red, puffy and tender, or have your closest friends start to avoid you because of bad breath? Any experiences with these symptoms may indicate that you have gum disease.
You may think that, at the very most, you may lose your teeth, but there are emerging evidence that gum disease is also linked to heart disease and preterm low birth weight babies.
Gum disease starts as a result of poor oral hygiene or cigarette smoking, allowing bacteria to invade your gum and produce toxins that cause a separation between the roots of your teeth and the supporting bone. Over time, your teeth will start to appear longer and the mobility increases cause spaces to open.
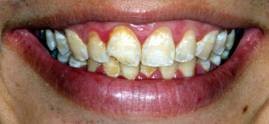 Bleeding - Gingivitis
Bleeding - Gingivitis
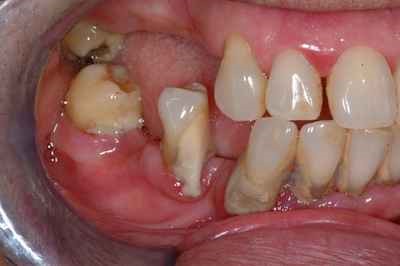 Periodontitis: Severe gum problems causing drifting of teeth and tooth loss
Periodontitis: Severe gum problems causing drifting of teeth and tooth loss
The paediatric dentists specialise in training young children to accept dental treatment. Children who would especially benefit from the long term care of a paediatric dentist include those who are at high risk of developing dental disease and children with special needs.
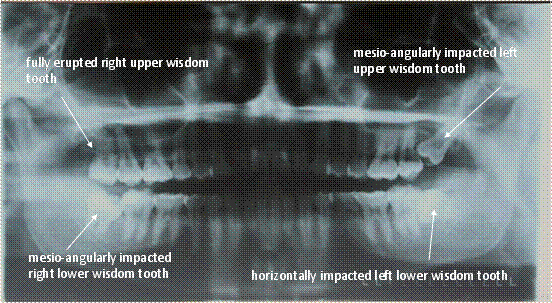
The surgical removal of impacted (and buried) teeth is one of the most common oral surgical procedures carried out by an oral and maxillofacial surgeon. Examples of impacted teeth include the wisdom teeth (third molars), upper canines and lower premolars.
Most of these teeth are buried in the bone and have to be surgically removed if they cause pain. Other indications for removal include pathology such as cysts and for orthodontic reasons. These procedures can be carried out in the outpatient clinics, or under general anaesthesia as a day surgery or overnight stay in the hospital.
Includes chin surgery, rhinoplasty, soft tissue orofacial surgery and more.
Maxillofacial injuries comprise injuries to the facial bones, oral and facial soft tissues, as well as the teeth.
These injuries can occur as a result of road traffic accidents, domestic violence or industrial accidents. It can range from relatively minor ones, which can be treated on an outpatient basis, to severe injuries which require hospital admission and surgery.
These injuries are treated by the oral and maxillofacial surgeon and there is a 24-hour service available for the diagnosis and management of these cases.
Teeth can be lost as a result of dental decay, gum disease and dental trauma. The condition of missing one or more teeth is called edentulism.
Missing teeth can be replaced in a number of ways including dentures, bridges or implants.
Dental implants are artificial tooth root replacements and are used to support restorations that resemble a tooth or group of teeth.
The dentist will assess the individual situation and recommend the appropriate restoration for you.
Teeth can be lost as a result of dental decay, gum disease and dental trauma. The condition of missing one or more teeth is called edentulism.
Missing teeth can be replaced in a number of ways including dentures, bridges or implants.
Dental implants are artificial tooth root replacements and are used to support restorations that resemble a tooth or group of teeth.
The dentist will assess the individual situation and recommend the appropriate restoration for you.
Bridges
Dentures
Implants
Oral mucosal disease involves the soft tissues of the mouth including the lips, gums, cheek, tongue, palate and even the salivary glands. These oral lesions can present in the mouth as swellings, white or red patches or even as ulcers, and can be a manifestation of systemic conditions.
It is important to have these lesions examined by an oral and maxillofacial surgeon as some of these lesions may also be cancerous. The oral and maxillofacial surgeon may perform biopsies of these lesions if they appear suspicious and will also be involved in the treatment of such diseases.
Oral cancer is a deadly disease of the face, mouth and jaws. Its diagnosis and management is by a multi-disciplinary team involving the oral and maxillofacial surgeon, the radiation oncologist, medical oncologist, maxillofacial prosthodontist and restorative dentist, speech and swallowing therapist, and dietitian.
The patient with oral cancer will be seen at the Dental Oral Cancer Clinic for diagnosis, treatment planning and follow-up to ensure the patient has a good quality of life after treatment.
The oral and maxillofacial surgeon is involved in the surgical treatment of cancer resection and reconstruction, and helps in the oral rehabilitation of function such as chewing and swallowing with dental implants, together with the maxillofacial prosthodontist. The patient will also be on follow-up for any future dental and oral related problems.
Infection of the teeth and soft tissues of the mouth including salivary glands may result in facial swelling, pain and a limitation in mouth opening. If left untreated, these infections may become very serious and can even be life-threatening.
These orofacial infections are normally treated by an oral and maxillofacial surgeon and the treatment involves surgical drainage, removal of the source of the infection (e.g. extraction of the causative tooth) and antibiotic therapy.
Endodontic services include endodontic treatment, retreatment, endodontic surgery, bleaching discolored teeth, treating traumatic injuries, as well as diagnosing and treating pain.
At times, standard endodontic treatment is ineffective and a surgical procedure is needed to remove the infected pulp and seal the root canal from the tip of the tooth. This surgical procedure is performed after the completion of the endodontic treatment.